UiPath: An Introduction to Robotics Process Automation

Aljohn De Guzman
Meet Nancy!

HR Officer
Meet Nancy!

- 200+ CVs per day
- Extracts necessary information from CV to HR System
Meet Nancy!

- 5 mins / CV
- Less than 2hrs to finish
Meet Bob the Robot!
Can do the same job in less than 20 mins
Robotics Process Automation
R obotics
P rocess
A utomation
Robotics Process Automation
Robotic process automation (or RPA) is an emerging form of clerical process automation technology based on the notion of software robots or artificial intelligence (AI) workers.
Software 'Robot'
A software 'robot' is a software application that replicates the actions of a human being interacting with the user interface of a computer system.
RPA vs AI
RPA is a software robot that mimics human actions, whereas AI is the simulation of human intelligence by machines.
RPA vs AI
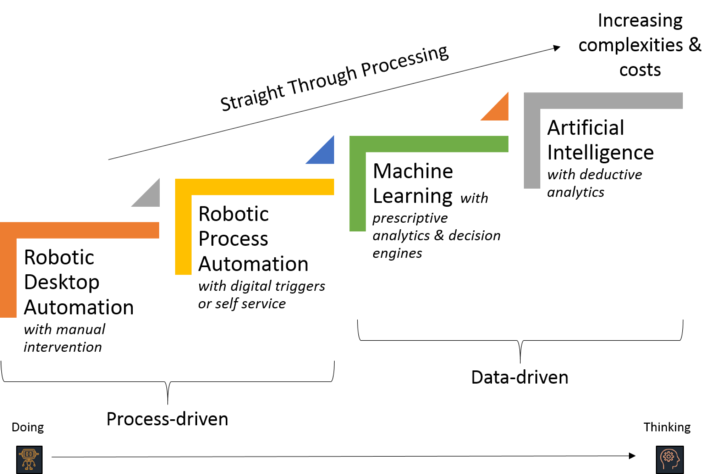
Use-Cases
- Execution of data entry into an ERP system
- Operates on the user interface (UI) in the same way that a human would
- Full end-to-end business
Characteristics of RPA
- Does not require programming skills.
- Can work with multiple system environment.
- Works well with well-defined rule-based process.
- Works well with repeatable rule-based transactions.
Benefits
-
Accuracy & Quality
- Minimization/ elimination of errors
-
Granular process monitoring
- Can record/analyze/optimize every action of a live robotic process
-
Less labor dependent
- No wage inflation
- Focus on less, but better skilled employees
Benefits (cont.)
-
Scalability & Flexibility
- Reusable components; scale much better than approaches for screen scrapping, macros and scripts.
-
No information loss
- Can record/analyze/optimize every action of a live robotic process
-
Reduce risk
- Processes become more manageable
Benefits (cont.)
-
Continuity/ Tirelessness of machines
- Seamless work 365/24/7 without people fatigue or quality variance
- Cost Reduction
-
Higher Speed and Throughput
- Can deliver proof-of-concept in a few months at first time; within a few weeks after going through the learning!
Human vs. Robot Process Execution
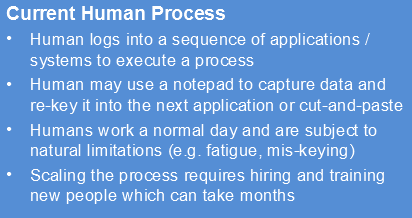
Human vs. Robot Process Execution
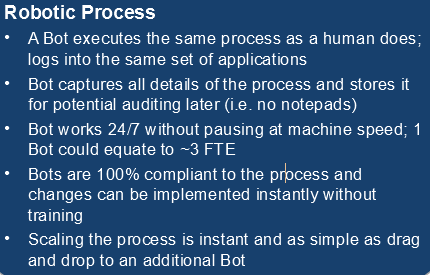
Benefits (cont.)
-
Less IT support needed
- Seamless work 365/24/7 without people fatigue or quality variance
-
Business Continuity
- Ability to route work to alternative servers/ computers in other locations
-
Security
- Reduce/ minimize human factor for fraud, intrusion and malpractice
When to use RPA?
- Could the problem be solved by changing the business process?
- Is it a manual process with enough volume or compliance risk to justify automation?
- Does the process involve structured or unstructured data?
- Is it a rules-based process, or does it require human judgement?
- Are there a high number of “exceptions” in this process?
Common RPA Tools
- Blue Prism
- Automation Anywhere
- UiPath





Flowcharts & Sequences
Sequences
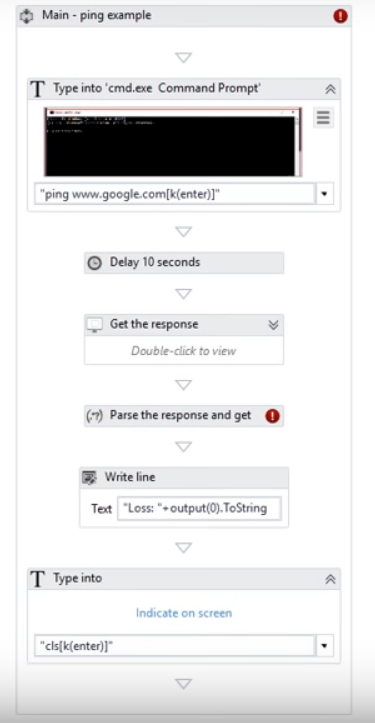
Sequences are the smallest type of project.
They are suitable to linear processes as they enable you to go from one activity to another seamlessly, and act as a single block activity
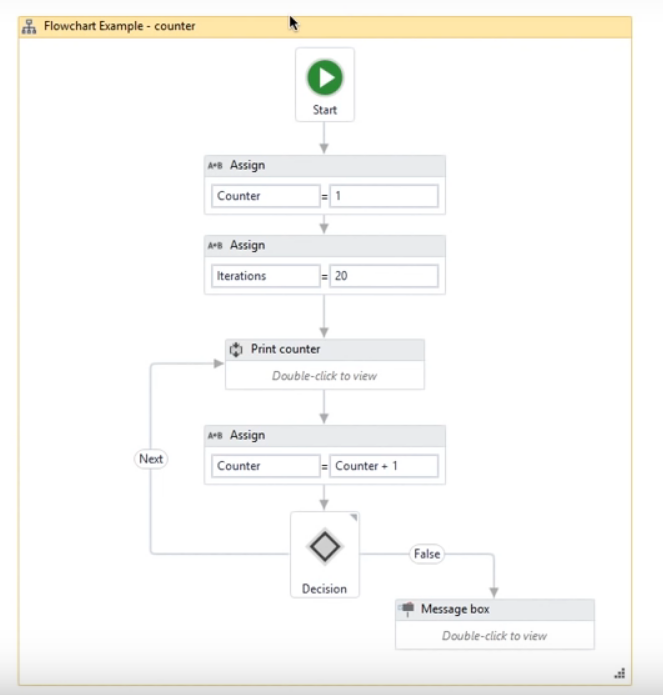
Flowcharts
Flowcharts can be used in a variety of settings, from large jobs to small projects that you can reuse in other projects.
Unlike sequences, they present multiple branching logical operators, that enable you to create complex business processes and connect activities in multiple ways.
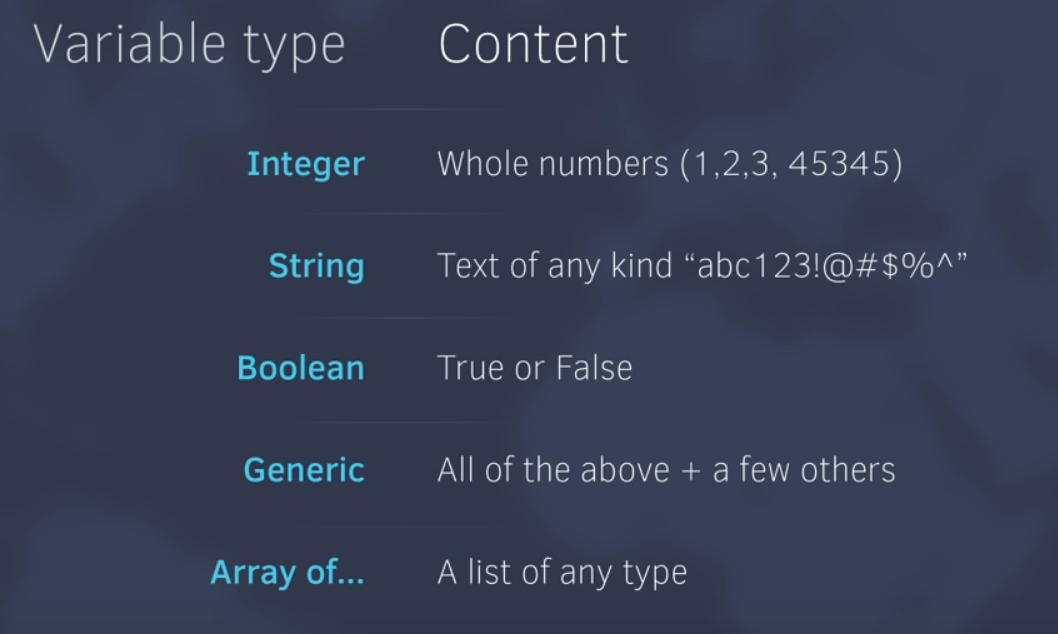
Variables
UiPath Varibles can hold:
- Text
- Numbers
- Files
- Images
- Others
Data Types
"Hello World, Hello UiPath"
Create a Flowchart Activity that will output a Message Box with a text "Hello World, Hello UiPath!
Exercise 1
"Read PDF
Create a Flowchart Activity that will output a Message Box with a text "Hello World, Hello UiPath!